In simple terms, a neutralization reaction is a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react with each other to produce water and a salt. This type of reaction typically results in a solution that is closer to neutral in pH, meaning it’s not as acidic or basic as the original reactants.
What is an Acid and a Base?
- Acid: A substance that releases hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water. For example, hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- Base: A substance that releases hydroxide ions (OH⁻) when dissolved in water. For example, sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
What Happens in a Neutralization Reaction?
In a neutralization reaction:
- The hydrogen ions (H⁺) from the acid combine with the hydroxide ions (OH⁻) from the base to form water (H₂O).
- The remaining ions from the acid and the base form a salt.
Example of a Neutralization Reaction:
Let’s take the example of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Reactants:
- Acid: Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Base: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- Reaction:
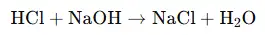
- Products:
- Water (H₂O)
- Salt: Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Name of the Salt Produced:
The salt produced in this reaction is sodium chloride (NaCl), which is the common table salt.
Summary:
In the reaction above, hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide neutralize each other to form water and sodium chloride. This is why it’s called a neutralization reaction—because the acid and base cancel each other out, creating a more neutral product.


